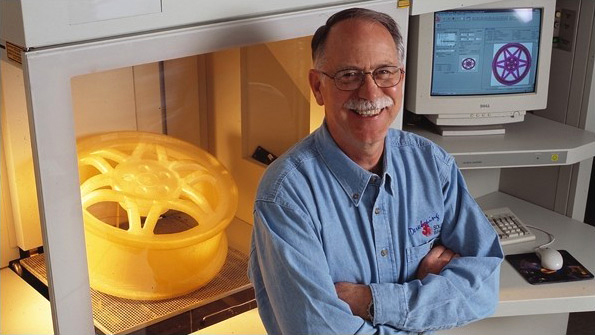
The next important achievement was the invention of the FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) method or modeling by melting, patented by Steven Scott Crump, co-founder of Stratasys, in the late 1980s. The FDM technology operates on the principle of extruding melted plastic through a nozzle to layer objects. This technology became the foundation for a wide range of industrial printers and most of the desktop 3D printers available today for a wide audience.

The 1990s marked further development and commercialization of 3D printing. New technologies such as SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) and DLP (Digital Light Processing) were developed and introduced, expanding the possibilities of additive manufacturing, including the use of a wider range of materials such as metals, ceramics, and composites.
At the beginning of this century, 3D printing rapidly gained popularity not only among engineers and designers but also in broader circles, thanks to the simplification and reduction in the cost of technologies. A key moment was the expiration of patents on key technologies, which led to a surge in innovation and the emergence of numerous startups offering affordable 3D printing solutions.
Today, 3D printing is an integral part of the manufacturing process in many industries, offering solutions for creating prototypes, end products, personalized items, and complex solutions that are difficult or impossible to manufacture by traditional methods. The development of additive technologies continues, promising even more innovative solutions and opportunities in the future.
In Israel, a country known for its technological innovations, 3D printing is rapidly gaining popularity, becoming an integral part of the industrial and technological landscape. In this dynamically developing environment, our company, One Logic Lab, offers a wide range of services in 3D printing, including 3D scanning and 3D modeling (prototyping and reverse engineering). We use advanced printing technologies, such as FDM (FFF) and SLA (DLP), ensuring high quality and precision of our products. Our services are aimed at providing our clients — both individuals and corporate customers — with innovative solutions that help realize their most ambitious projects.